偏波保持フォトニック結晶光ファイバ上に刻み込まれた長周期光ファイバ格子を用いた曲げ不感歪・温度同時測定
引用
Kim, DK, Lee, SL, Choi, S., Kim, MS, Kim, J., Han, J., & Lee, YW (2020). 偏波保持フォトニック結晶ファイバー上に刻み込まれたカスケード接続された長周期ファイバーグレーティングに基づく、曲げに影響を受けない歪みと温度の同時測定.韓国物理学会誌, 76 (9), 810-818. doi: 10.3938/jkps.76.810
キーワード
- 光ファイバー装置
- 長周期光ファイバ格子(LPFG)
- 偏波保持フォトニック結晶ファイバー(PMPCF)
- 曲げに鈍感
- 同時測定
- 歪み
- 温度
- カスケードLPFG
- 複屈折
- 分極
- センサーヘッド
- 干渉スペクトル
- センサーインジケーターディップ(SID)
- CO2レーザー刻印
- 有効屈折率
- 波長シフト
- 交差感受性
- モード結合
- ファイバー内マッハ・ツェンダー(MZ)干渉計
簡単な
この記事では、歪みと温度を同時に測定するために、偏波保持フォトニック結晶ファイバー上にカスケード接続された長周期ファイバーグレーティングを使用した、曲げに鈍感な光ファイバーセンサーの開発と実証について報告します。
まとめ
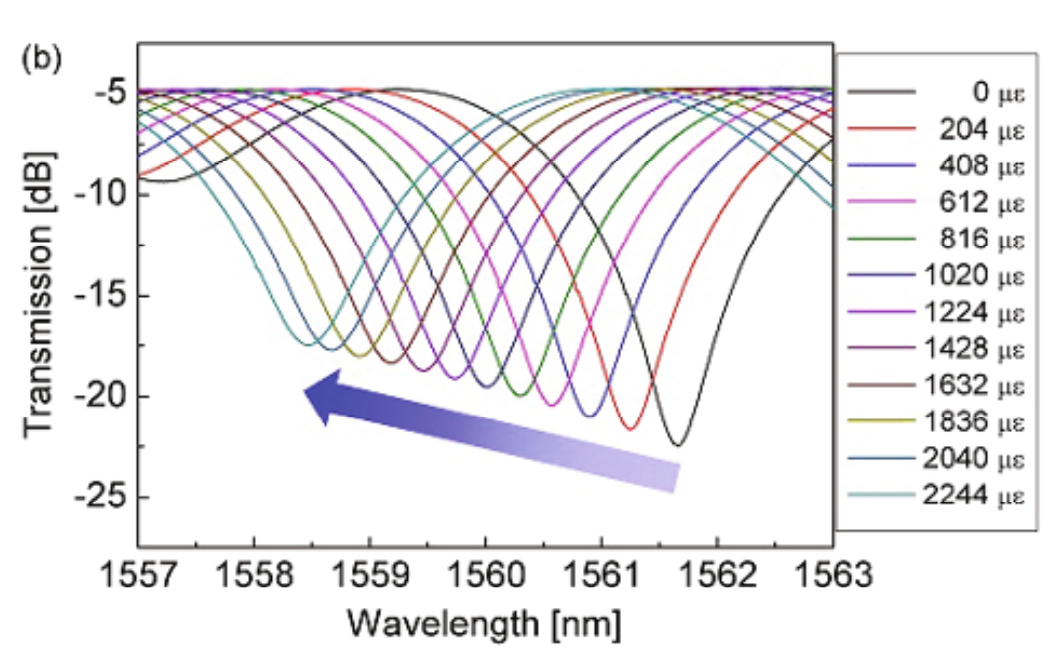
本論文では、偏波保持フォトニック結晶ファイバ(PMPCF)上に刻み込まれたカスケード接続された長周期ファイバグレーティング(LPFG)を用いた、新しい光ファイバセンサを紹介する。このセンサは、直交する偏波状態から得られる2つのセンサインジケータディップ(SID)の波長シフトを解析することで、歪みと温度の変化を良好な直線性で独立して測定することができる。このセンサは曲げに対する感度が低いため、曲げが発生する可能性のある環境下でも同時かつ安定した測定が求められる実用アプリケーションへの有力な候補となる。
出典: https://sci.bban.top/pdf/10.3938/jkps.76.810.pdf#
