中空コア光ファイバ接続構造に基づく曲率温度センサ
引用
徐心怡、周蕊、李瑞、李飞、刘颖刚。 (2025).空芯光ファイバ接続構造に基づく曲率温度センサ [中空コア ファイバ接続構造に基づく曲率温度センサ].光電子技術応用[電気光学技術応用]、 40 (1)、58-62。
キーワード
- 光ファイバーセンサー
- 曲率センサー
- 温度センサー
- 中空コア光ファイバー(HCF)
- コアレスファイバー(NCF)
- シングルモードファイバー(SMF)
- スプライシング構造
- マッハツェンダー干渉計 (MZI)
- ファブリペロー干渉計(FPI)
- 感度
- 波長ドリフト
- 権力の変化
- 干渉スペクトル
- バイオメディカル
- 材料試験
- ケーブル監視
- 石油とガス
- 航空宇宙
- 工業生産
簡単な
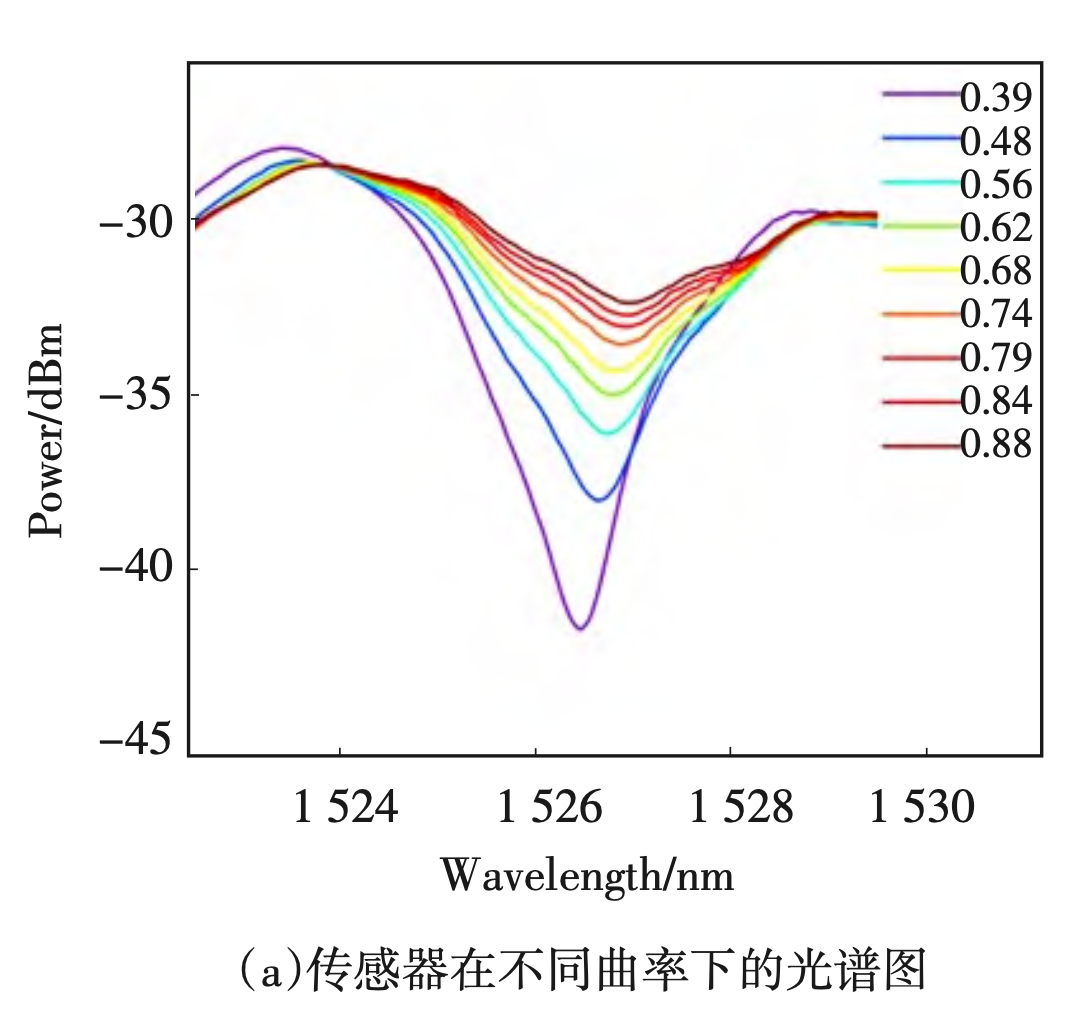
この記事では、曲率と温度を同時に測定し、温度に対して 64.7 pm/℃、曲率に対して27.044 dBm/m- 1の最大感度を達成した、マッハ・ツェンダー干渉計 (MZI) とファブリ・ペロー干渉計 (FPI)を組み合わせた接合中空コアファイバー構造に基づく高感度かつ低コストの光ファイバーセンサーの設計と実験検証を紹介します。
まとめ
研究者らは、中空コア光ファイバーと無コア光ファイバー、およびシングルモード光ファイバーを接合することで、低コストで高感度な光ファイバーセンサーを設計・構築した。この構造は、マッハ・ツェンダー干渉計とファブリ・ペロー干渉計を組み合わせ、干渉スペクトルのパワーと波長の変化を検出することで、曲率と温度を同時に測定する。このセンサーは、温度に対して64.7 pm/℃ 、曲率に対して27.044 dBm/m-1の最大感度を達成し、優れた再現性と安定性を示しており、バイオメディカル、材料試験、産業用モニタリングなどの分野での活用が期待される。
起源:
