熱成形された二重クラッドファイバーにおける低OH拡散を設計するための効率的なアプローチ
引用
Jasim, AA, Peterka, P., Podrazký, O., Kamrádek, M., Todorov, F., & Honzátko, P. (2021).熱成形ダブルクラッドファイバーにおける低OH拡散設計のための効率的なアプローチ。 光ファイバー技術、 63、102513。https ://doi.org/10.1016/j.yofte.2021.102513
キーワード
- ダブルクラッドファイバー(DCF)
- CO2レーザー
- 光ファイバープリフォーム
- クラッディング成形
- 高出力ファイバーレーザー
- マルチモードファイバー
- ヒドロキシル基(OH)
- OH拡散
- フッ化水素酸(HF)エッチング
- 水分ピーク(1383 nmでのOH吸収を参照)
- 光減衰
- 表面散乱
- MCVD(改良化学蒸着法)
- カットバック法(減衰測定用)
- ヘレウスF300シリカロッド
- 低屈折率ポリマーコーティング
- アブレーション(CO2レーザーによる)
- 熱物理的効果
簡単な
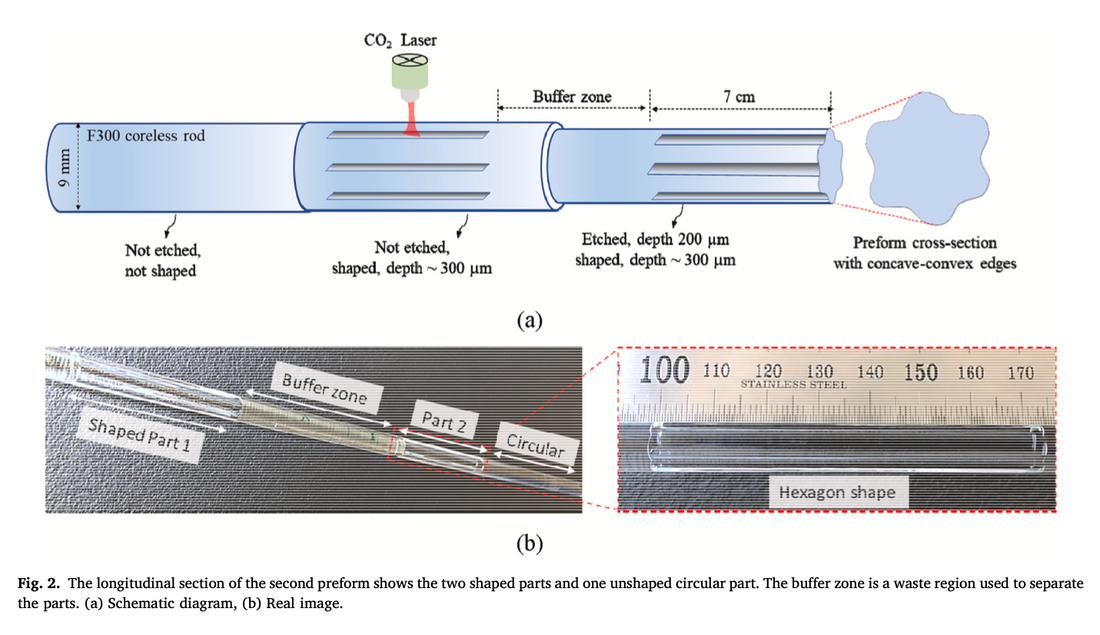
この記事では、CO2 レーザー成形の前にフッ化水素 (HF) 酸でエッチングして熱成形された二重クラッド ファイバー プリフォーム内のヒドロキシル (OH) 拡散を減らし、線引きされたファイバー内の OH 関連の減衰を低減する効率的なアプローチを紹介します。
まとめ
CO2レーザーを用いて成形されるダブルクラッド光ファイバー(DCF)における水酸基(OH)汚染を低減するため、研究者らは光ファイバー母材をフッ化水素酸(HF)エッチングで前処理し、OHを含む表面層を除去しました。この方法により、未処理の母材と比較して、最終的な光ファイバーにおけるOH関連の減衰が43%も効果的に低減しました。同時に、表面散乱を低く抑え、複雑な形状に対するCO2レーザー成形の利点も維持しました。
起源:
