還元グラフェン酸化物ベースの中間層を用いた光ファイバ偏光ビームスプリッター
引用
Koo, J.; Park, J.; Song, Y.-W.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.; Lee, JH (2015).還元酸化グラフェンベースの中間層を用いた光ファイバー偏光ビームスプリッター. 光学材料、 46、324–328。https : //doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2015.04.039 .
キーワード
- 光ファイバー偏光ビームスプリッター(PBS)
- 還元酸化グラフェン(rGO)
- 金属中間層材料
- カプラ構造
- 側面研磨繊維
- 横磁気(TM)表面波
- 偏光消光比
- 動作帯域幅
- 酸化グラフェン(GO)
- 紫外線(UV)照射による還元
- TMモード
- TEモード
- 表面プラズモンポラリトン
- 挿入損失
- 可変波長レーザー
- 偏光計
- 半波長板
- 誘電体GOスプレー
簡単な
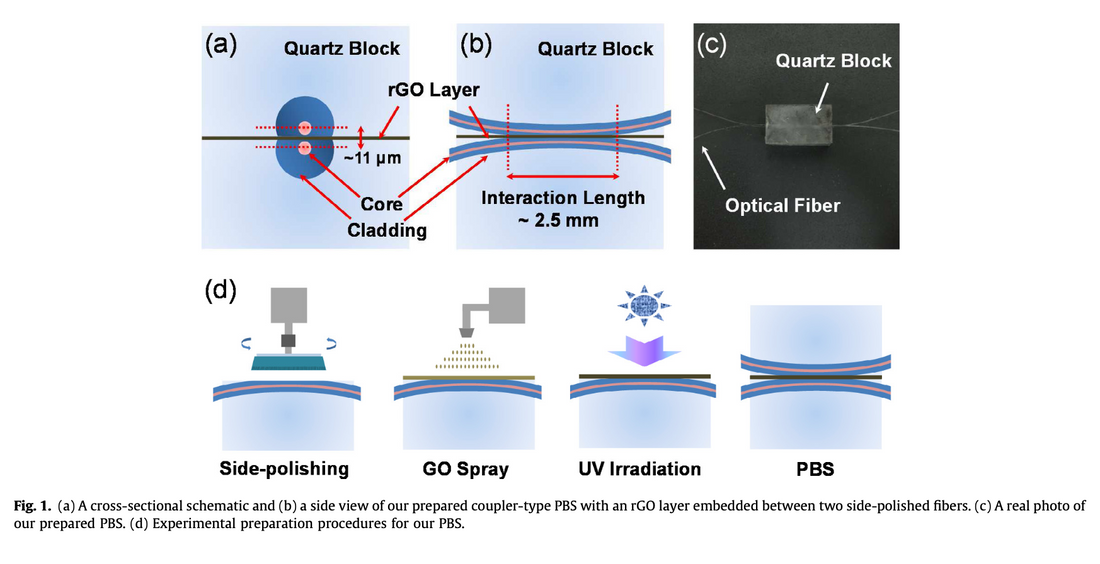
この記事では、 TM 表面波誘導に基づく偏光ビーム分割を実現するためにカップラー構造に還元グラフェン酸化物 (rGO) 中間層を使用し、 14.5 dBの偏光消光比と少なくとも 100 nm の動作帯域幅を示す光ファイバー偏光ビームスプリッター (PBS) を提案し、実証します。
まとめ
本稿では、 2本の側面研磨された光ファイバーの間に還元グラフェン酸化物(rGO)中間層を用いて作製した光ファイバー偏光ビームスプリッター(PBS)について紹介する。GOスプレーと紫外線照射によって形成されたrGO層は、 TM表面波の誘起を通じて偏光ビーム分割を可能にする。作製したPBSは、 1550 nmで14.5 dBの偏光消光比と、少なくとも100 nm(1500~1600 nm)の動作帯域幅を示した。本研究は、低コストのrGOを用いて光ファイバーPBSデバイスを作製できる可能性を示している。
出典: https://sci.bban.top/pdf/10.1016/j.optmat.2015.04.039.pdf#
