従来の光ファイバに統合された光制御可変光ファイバ減衰器
引用
Martincek, I., Pudis, D. (2014).従来の光ファイバーに統合された光制御可能な可変光ファイバー光減衰器. オプティック、 125 (20)、7085–7088。 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2014.08.097
キーワード
- 光学的に制御可能
- 熱光学効果
- 液体被覆
- 光ファイバー
- 減衰
- レーザー放射
- 屈折率のコントラスト
- コア・クラッド界面
- 加熱要素
- フューズドシリカ
- ミネラルオイル(カーギル液体)
- 静的依存
- 動的応答
- 立ち上がり時間
- 秋の時間
- 挿入損失
- シングルモード光ファイバー
- 通信用光ファイバー
簡単な
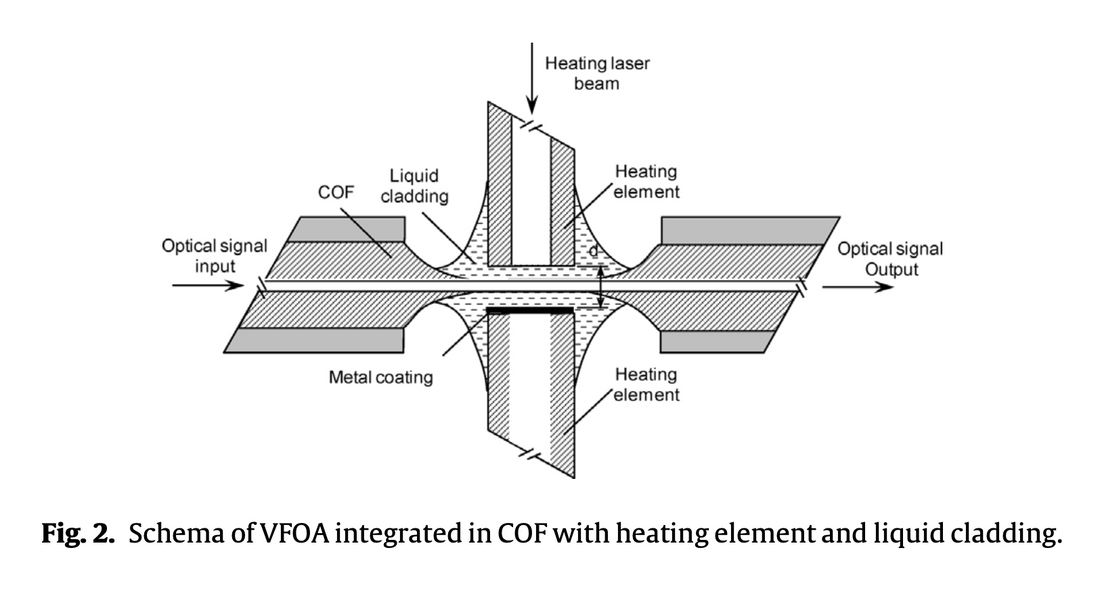
この記事では、従来の光ファイバーに統合された、レーザー放射によって加熱された液体クラッド内の熱光学効果を利用して屈折率コントラストを変化させ、伝播信号の減衰を制御する、新しい光学的に制御可能な可変光ファイバー光減衰器について説明します。
まとめ
本稿では、標準的な光ファイバーに統合された、新しいタイプの光制御型可変光ファイバー減衰器(VFOA)について説明します。このデバイスは、液体クラッド(鉱油)の熱光学効果を利用して減衰を制御します。レーザーが金属層を加熱し、それが液体クラッドを加熱することで、コアとクラッドの界面における屈折率コントラストが変化し、伝播する光信号のパワーに影響を与えます。VFOAは、立ち上がり時間24ミリ秒、立ち下がり時間159ミリ秒で最大-12dBの減衰を達成しました。これは、全光ネットワークや光ファイバーセンサーへの応用が期待されます。
出典: https://sci.bban.top/pdf/10.1016/j.ijleo.2014.08.097.pdf#
