氷支援電子ビームリソグラフィーに基づく無溶媒ナノファブリケーション
引用
Hong, Y., Zhao, D., Wang, J., Lu, J., Yao, G., Liu, D., Luo, H., Li, Q., & Qiu, M. (2020). 氷支援電子ビームリソグラフィーに基づく溶媒フリーナノファブリケーション. Nano Letters , [抜粋に巻号情報が明記されていない場合はDOIを参照] . doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c03809
キーワード
- 無溶媒ナノ加工
- 氷支援電子ビームリソグラフィー(iEBL)
- 氷のリソグラフィー
- 電子ビームリソグラフィー(EBL)
- ナノファブリケーション
- 光ファイバー装置
- 3Dナノ構造
- 蒸着
- 電子抵抗としての氷
- 昇華
- ブローオフプロセス
- 化学物質汚染の回避
- 非平面基板
- 屈折率センサー
- プラズモニックナノディスクアレイ
- 走査型電子顕微鏡(SEM)
- 金属堆積チャンバー(MDC)
- 極低温サンプルホルダー
- 電子刺激脱離
- 水分子の断片化
- 残留引張応力
簡単な
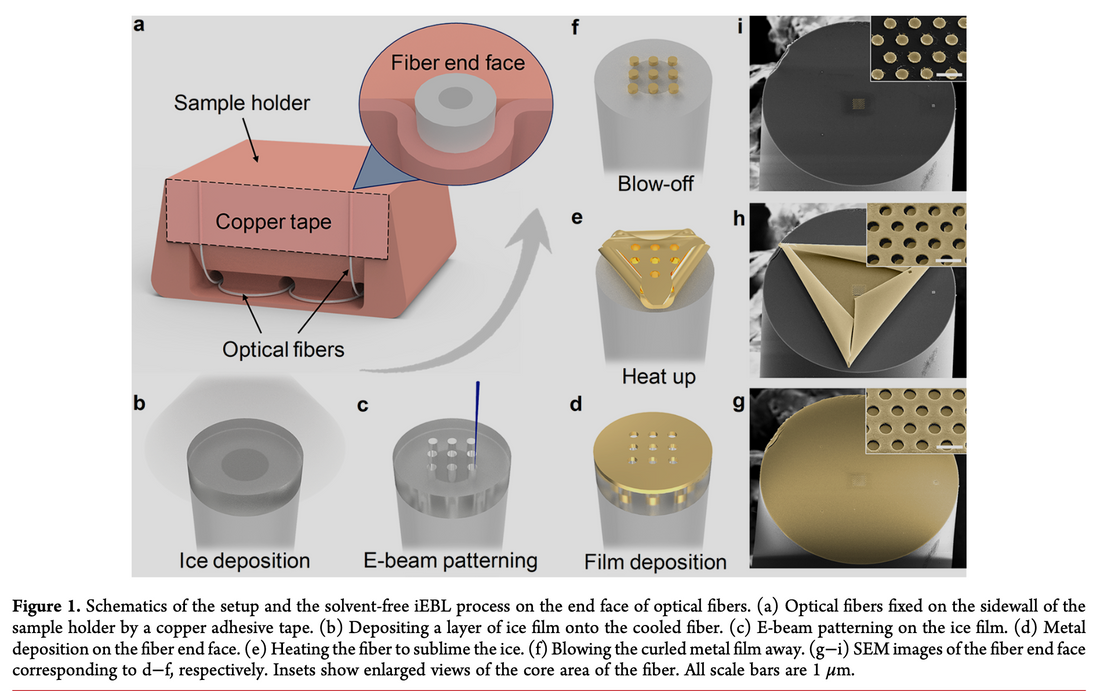
本稿では、電子ビームリソグラフィーの電子レジストとして氷を使用する溶媒を使用しないナノ加工法を紹介し、光ファイバーなどの非平面基板上で繊細なナノ構造や屈折率センサーを作成するための適用可能性を示します。
まとめ
本論文では、水氷を電子線レジストとして用いる、溶媒を使用しない新しいナノファブリケーション手法である氷支援電子ビームリソグラフィー(iEBL)を紹介する。この手法はプロセスを簡素化し、化学汚染を回避し、光ファイバーのような任意の形状の基板上でのナノファブリケーションを可能にする。著者らは、シングルモードファイバーの端面に繊細なナノ構造、準3D構造、そして機能的な屈折率センサーを作製することで、iEBLの汎用性を実証している。
出典: https://sci.bban.top/pdf/10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c03809.pdf#
