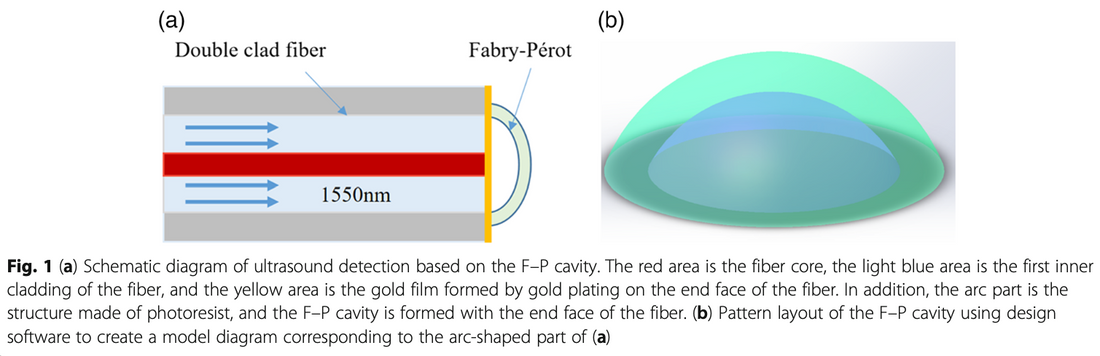
Ultrasonic signal detection based on Fabry– Perot cavity sensor
Citation
Yang, W., Zhang, C., Zeng, J., & Song, W. (2021). Ultrasonic signal detection based on Fabry– Perot cavity sensor. BioMedical Engineering OnLine, 20(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42492-021-00074-0
Keywords
- Ultrasonic sensor
- Fabry-Pérot microcavity
- Double-clad fiber (DCF)
- Acoustic sensor
- Endoscopic photoacoustic imaging
- Two-photon 3D lithography machine
- Full-optical detection
- Photoacoustic imaging
- Photoacoustic endoscopy
- Biomedical information technology
- Medical diagnosis
- Miniaturization
- High sensitivity
- Large bandwidth
- Polymer material
- Optical elastic coefficient
- Deformability
- Flat-concave F–P polymerization cavity
- Reflectivity
- Cavity length
- Laser scanning
Brief
This article describes the development and experimental validation of a miniaturized ultrasonic sensor based on a Fabry-Pérot cavity fabricated on the end face of a double-clad fiber using two-photon three-dimensional lithography, demonstrating its feasibility for high-precision ultrasonic signal detection with potential applications in biomedical imaging, particularly photoacoustic endoscopy.
Summary
Researchers developed a tiny, highly sensitive ultrasonic sensor based on a Fabry-Pérot cavity fabricated on the end of a double-clad fiber using 3D printing for precise acoustic signal detection, particularly for use in miniaturized medical imaging tools like photoacoustic endoscopes to improve early disease diagnosis.
Origin: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42492-021-00074-0
